Misconceptions We Were Taught As Kids That Ended Up Completely False
Remember those wild and wacky “truths” your school teacher tried to instill in you as a kid? Truths such as “Twinkies last forever” and “daddy longlegs are actually spiders? It’s easy to be fooled as a youngster with playground rumors circulating around your brain. Well, worry no more—we’re here to help you separate the truth from fiction!
So, what really happens when you crack your knuckles? Keep reading to find out!
Coffee Consumption Doesn't Lead To Dehydration
It’s a common myth that a cup of coffee in the morning will leave you dehydrated for the rest of the day. Although research suggests that consuming coffee increases the frequency of your trips to the restroom, there is no evidence that it dehydrates you.

Source: Daniel Berehulak/Getty Images
Just take UCLA associate professor Dr. Daniel Vigil’s word for it. As he puts it, “When you drink that cup of coffee or glass of iced tea, just think of it as a dose of liquid courage with a bonus caffeine boost!”
Spiders And Daddy Longlegs Are Distinct From One Another
Though often mistaken for common spiders, daddy longlegs are actually members of the arachnid family, harvestmen. Contrary to popular belief, they are not spiders and have certain anatomical differences that give this away.
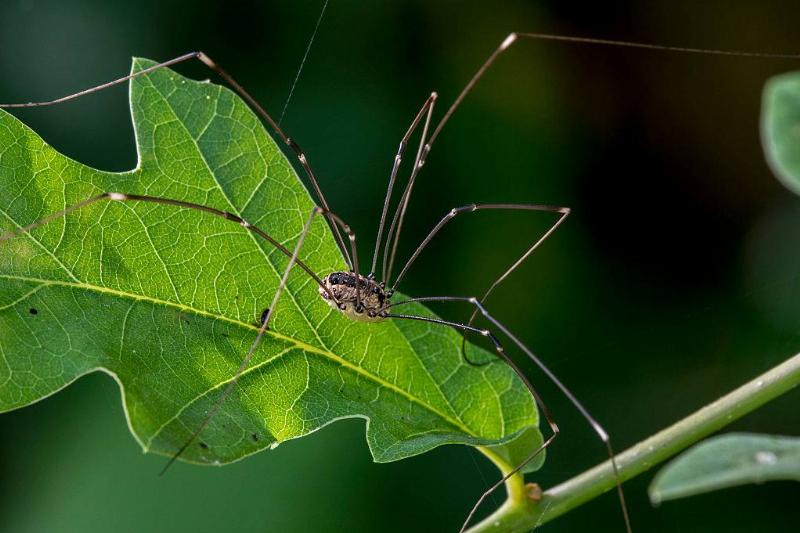

Source: Arterra/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
Unlike spiders, which typically have eight eyes, daddy longlegs only have two. Additionally, their heads and abdomens are fused together to form a single body cavity, while spiders have distinct head thorax and abdomen separations. These details help us understand why daddy longlegs should not be considered spiders or confused with them.
A Bloody Nose Won't Stop If You Tilt Your Head Back
Many “self-described” experts of medicine will advise you to tilt your head back to stop a bloody nose if one starts flowing. However, this line of thinking is flawed and will only result in you having swallowed a nose-worth’s amount of your own blood.

Source: Netflix
Treat a nosebleed appropriately by applying pressure to the nasal area for 20 minutes or so while sitting straight to prevent blood swallowing. They’re uncomfortable, but just keep in mind that tilting your head back won’t help and should actually be avoided if possible.
The following slide contains the real scoop about knuckle cracking!
Joint Issues Aren’t A Result Of Knuckle Cracking
Doctors say there is no link between cracking your knuckles and joint problems later in life. Some people find it pleasurable and a release of tension, while others may come off as irritable with the sound of knuckles cracking, which is presumably how this factoid got started.

Source: LILLIAN SUWANRUMPHA/AFP via Getty Images
The sound your knuckles make when popped is caused by the release of gases in your joint’s lubrication. While applying too much pressure could cause tendon damage, it is generally an infrequent occurrence. Just take it easy on those joints!
You Aren't More Prone To Catching A Cold During the Winter
Though it may seem like colder months leave us more vulnerable to certain illnesses, chilly weather doesn’t have to mean sickness! While many believe that cold weather increases your risk of developing a cold or the flu, it’s actually just a coincidence.

Source: Susann Prautsch/picture alliance via Getty Images
Is there any truth to this widespread belief? Shannon Fecher of UnityPoint Health clarifies that you can become ill due to frostbite and hypothermia, but this would be because these conditions weaken your immune system. In other words, staying warm and healthy is key to avoiding colds or the flu!
Twinkies Are Not Everlasting
When it comes to the shelf life of Twinkies, some people believe these treats live forever. But don’t believe everything you hear in the movies. Thanks to sorbic acid preservatives, these delicious snacks will remain fresh for about 25 days. After that, their texture and flavor may not be as good as it was beforehand.

Source: Sony Pictures Releasing
Don’t take our word for it—a school in Maine managed to keep a Twinkie for 40 years! Of course, its color and texture did change dramatically. Even with this example of extreme preservation, most Twinkies won’t last forever—so enjoy them while you can!
We Operate Beyond Ten Percent Of Our Intelligence
Although the belief that humans only use ten percent of their brains has been largely debunked, it’s still widely believed. Films like Lucy and Limitless have speculated about what could happen if we tapped into the other 90 percent, but such musings are just nonsense.

Source: Relativity Media
In the statement of Scientific American, neurologist Barry Gordon stated that the truth is that, at any given moment, most parts of the human brain are working. But there’s still reason to be hopeful —there’s always so much potential for human development!
Speaking of myths, here’s another one: Does gum stay in your stomach for seven years? Read on.
Gum Stays In Your Digestive System For Seven Years
Chewing gum is not intended for consumption, so to discourage ingestion issues, people commonly say that swallowed gum can remain in the system for up to seven years. While it’s true that gum isn’t designed to be broken down by digestion, it will usually pass through the body in a matter of days.

Source: Jim McIsaac/Getty Images
Despite that, that does not mean you should start swallowing your gum going forward—just don’t! Swallowing large amounts of gum may lead to medical complications, which you wouldn’t want to happen.
Vitamin C Is Not A Cure-All
Since the 1960s, there has been much debate surrounding whether “megadosing” on vitamin C can help people avoid common illnesses. Though it was formulated by Nobel Prize-winning chemist Linus Pauling (pictured), research since then has proven this theory untrue.
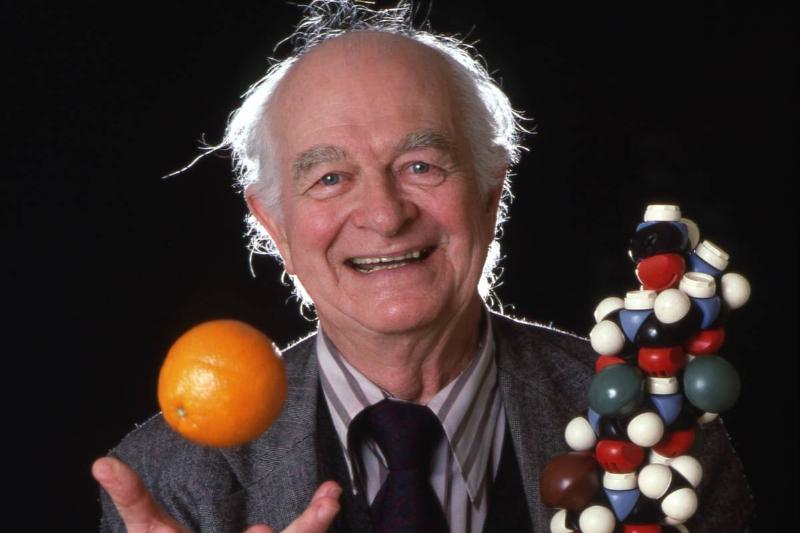
Source: Roger Ressmeyer/Corbis/VCG via Getty Images
While vitamin C may reduce the duration of a cold, it cannot protect a person from contracting one in the first place. Despite this widely-available information, supplement brands have created marketing campaigns based on the concept of megadosing—indicating the need for better consumer education on matters such as this.
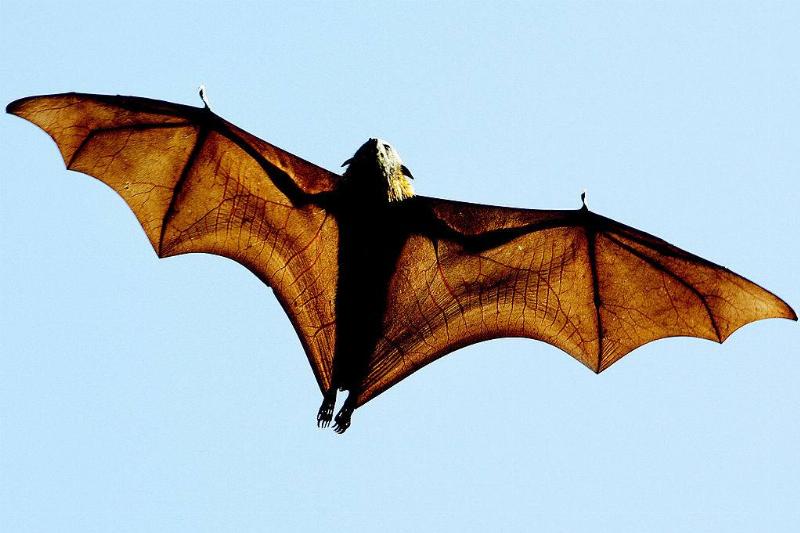
Bats Are Certainly Not Blind
In school, we often learn that bats use echolocation to compensate for their blindness. National Geographic has reported that some species of bats can actually see up to three times better than a human.

Source: GREG WOOD/AFP via Getty Images
Having said that, not all bats rely on echolocation to hunt for food; the so-called “megabats” or fruit bats do not use this form of perception at all to aid them in their hunt for sustenance. The more you know!
Now that you know about the incredible eyesight of our winged friends, we invite you to continue your exploration and discover what effect salt has on boiling water!
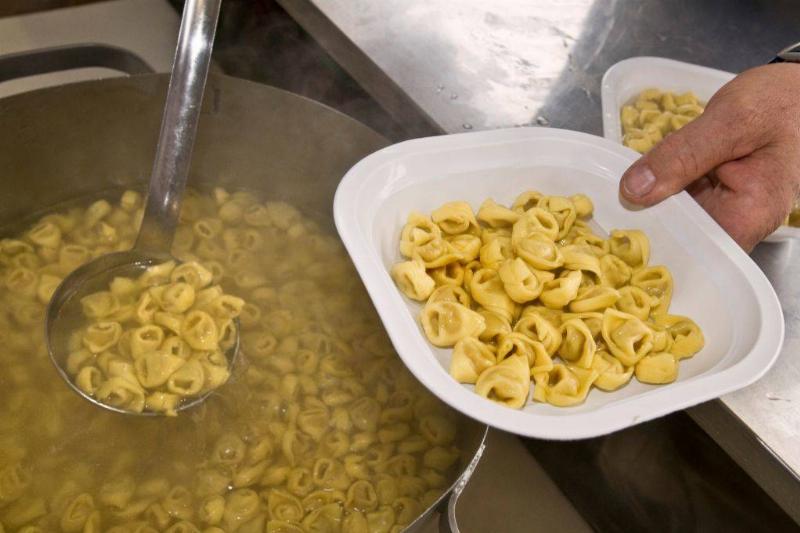
Salt Doesn't Speed Up The Water Boiling Process
We tend to believe that adding salt to water increases the speed of the boiling process. In fact, it actually slows it down because it raises the boiling point of the water. But interestingly, adding salt can make your pasta cook faster, but not because salt changes the pasta in any way.

Source: Hermes Images/AGF/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
The higher boiling point of the water caused by adding salt causes the pasta to cook faster, decreasing the necessary cooking time. This works with the smallest pinches of added salt—putting any more salt in your pot will not reduce cooking time any further.
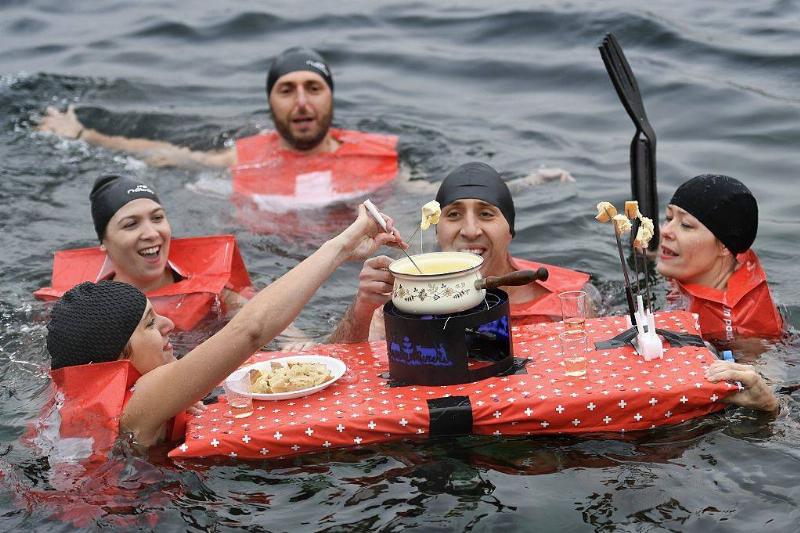
No, You’re Not Require To Wait 30 Minutes After Eating To Swim
The notion that you need to wait thirty minutes after eating before swimming has been proven false. In the past, it was thought that the blood in your body would be routed toward the gut and away from the limbs during the digestion process. This would make it more difficult for you to stay afloat and swim.

Source: FABRICE COFFRINI/AFP via Getty Images
Fortunately, this advice has never been accurate. But this factoid has been around for a while, as evidenced by the 1908 Boy Scout Handbook Scouting for Boys statement about taking half an hour before swimming, “You may drown—and it will be your own fault.”
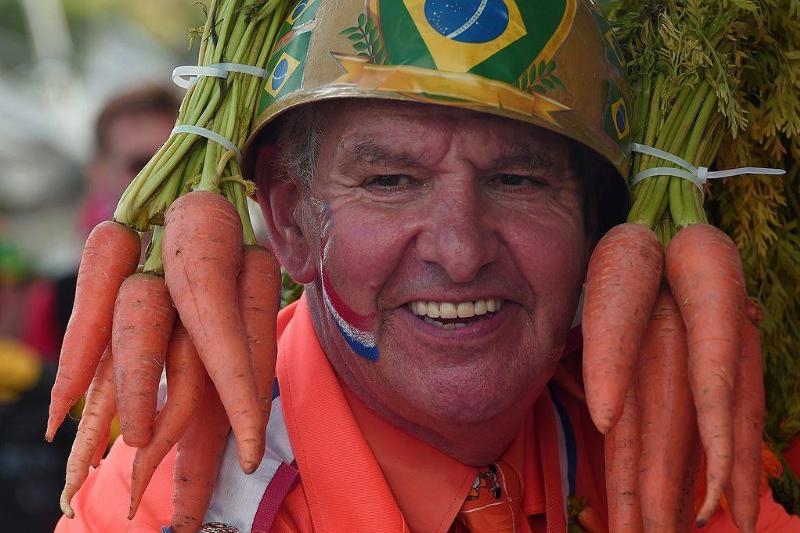
Carrots Won’t Improve Your Vision
Carrots have a well-established reputation for being beneficial for the eyes. This is due to their high levels of vitamin A, which helps sharpen vision in dim lighting. A deficiency in vitamin A may even result in blindness, making carrots an essential part of any balanced diet.

Source: DAMIEN MEYER/AFP via Getty Images
Nonetheless, it is important to remember that although they are beneficial to your eyes, don’t expect carrots to magically cure your vision deficiencies. So grab a carrot and stay informed on an array of nutrients for optimal eye health.
Uncover the truth if elephants really fear mice. Read on!
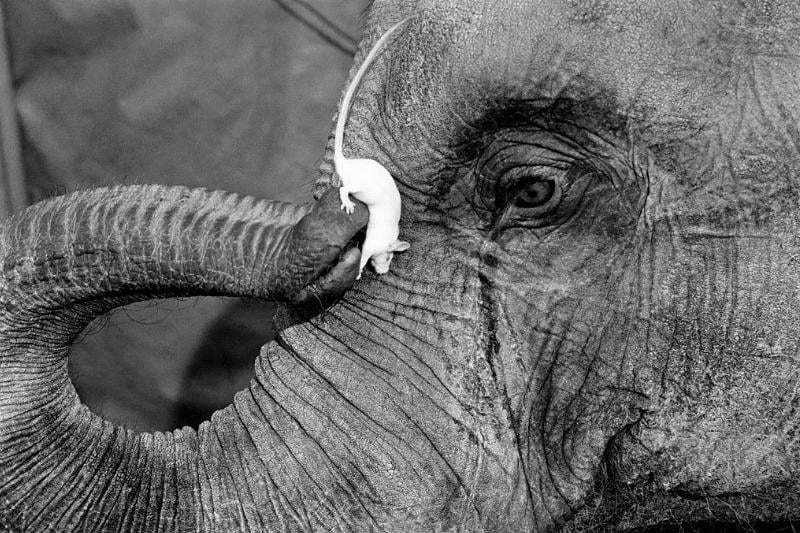
Mice Don’t Scare Elephants to Death
The whimsical movie Dumbo led many viewers to believe that elephants are frightened of mice. This is not accurate, as studies have shown that elephants are simply startled by a small, fast-moving animal and may react defensively—but they do not panic or run away in fear.

Source: WATFORD/Mirrorpix/Mirrorpix via Getty Images
Further research suggests that elephants possess poor eyesight and may simply be reacting naturally to an unexpected movement. Finally, experts on elephants will reassure you that mice are not a threat to elephants since they are very small.
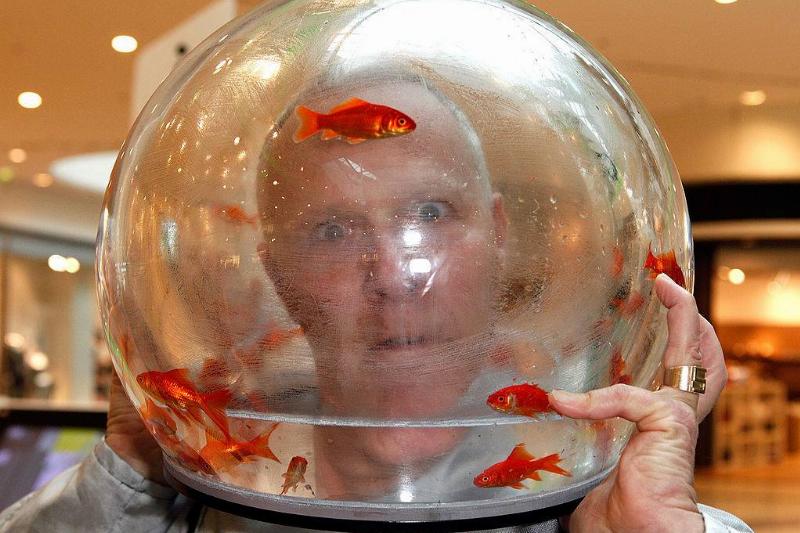
A Goldfish’s Memory Is Not Just Three-Seconds
Reports suggest that goldfish are capable of more than previously assumed, with evidence demonstrating the species’ longer-than-expected memory retention. Jamie Hyneman, from Mythbusters fame, managed to train his pet goldfish to navigate an obstacle course.

Source: Kristy Sparow/Getty Images
Furthermore, a study conducted at the University of Plymouth found that goldfish could operate a lever for a food reward and remembered when this lever was activated for one hour a day. These research findings point to possible advanced cognitive abilities in goldfish.
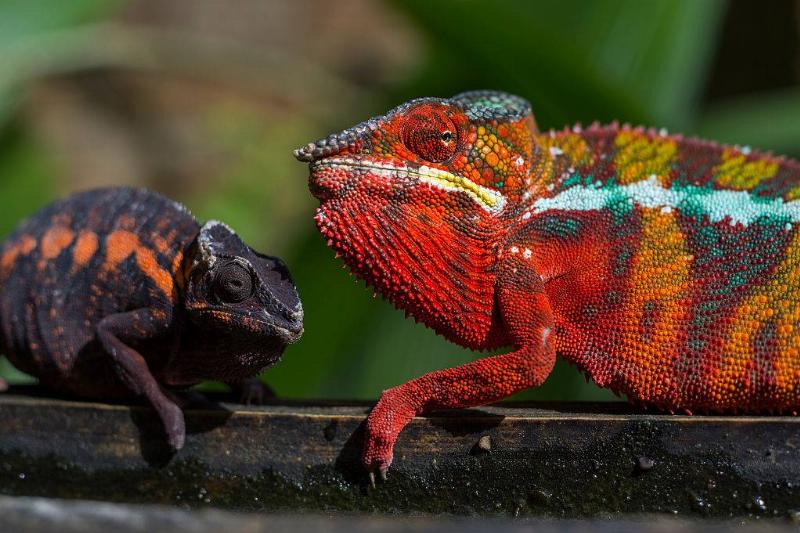
Chameleons’ Color Changes Aren't for Camouflage
Despite common perception, chameleons do not primarily change colors for defensive reasons—instead, they do it for social purposes or to attract mates. Chameleons have four layers of skin, three of which are colored and patterned in certain ways.

Source: Wolfgang Kaehler/LightRocket via Getty Images
Some have transparent crystals that reflect light and can create blue or white colors, while others have clear crystals that contain yellow, red, or black pigments. They can communicate feelings and responses to one another’s existing environments by altering the colors of these layers.
Melatonin Isn’t A Sleeping Pill Alternative
Sleep deprivation is a common issue for many people these days. A popular way to get off to Sleepytown is using melatonin, a naturally-occurring hormone. Often confused as a sedative, melatonin is taken in pill form. While it does help you get better rest, it’s not a sleeping pill.

Source: Ryan Pierse/Getty Images
Melatonin won’t make you fall asleep immediately, but it will help you secure a better night’s rest. However, if you do want to use this supplement, be warned—taking it on a regular basis can reduce your ability to stay asleep in the long run. It’s better to consult your doctor before taking sleeping supplements.
Do Dogs Actually Perspire?
After running around and playing for a long time, dogs do perspire—but their sweat glands are located in their paws. Sweating helps dogs to gain a better grip on the ground as moisture is released from their paw pads.
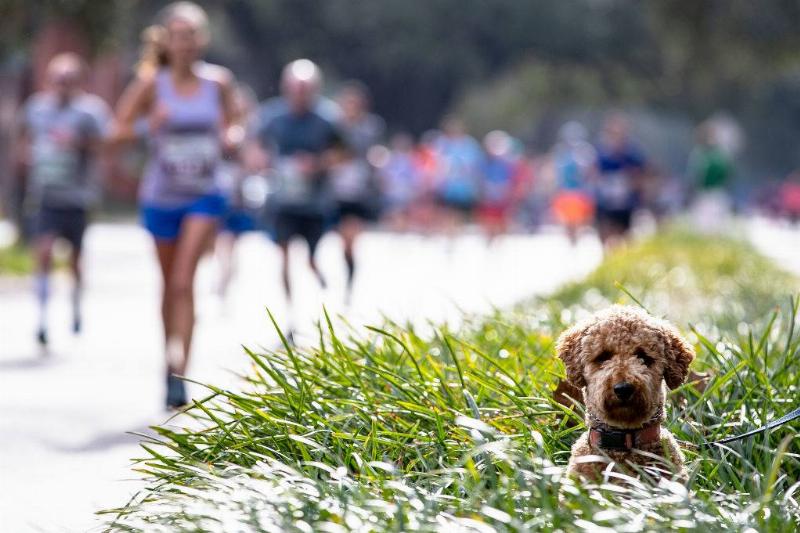

Source: Al Bello/Getty Images for Rock 'n' Roll Marathon
In order to keep themselves cool, dogs also let out evaporated water through their nasal passages and tongue by panting. This is why some people mistakenly think that their dogs don’t sweat.
Now answer this: what does a camel’s hump contain? To find out, move forward to the next slide.
A Camel's Hump Does Not Store Water
Contrary to popular opinion, camels do not store water in their humps—instead, it is used to store fat. Camels can hold up to eighty pounds of fat reserves and can go three weeks without needing to refuel.
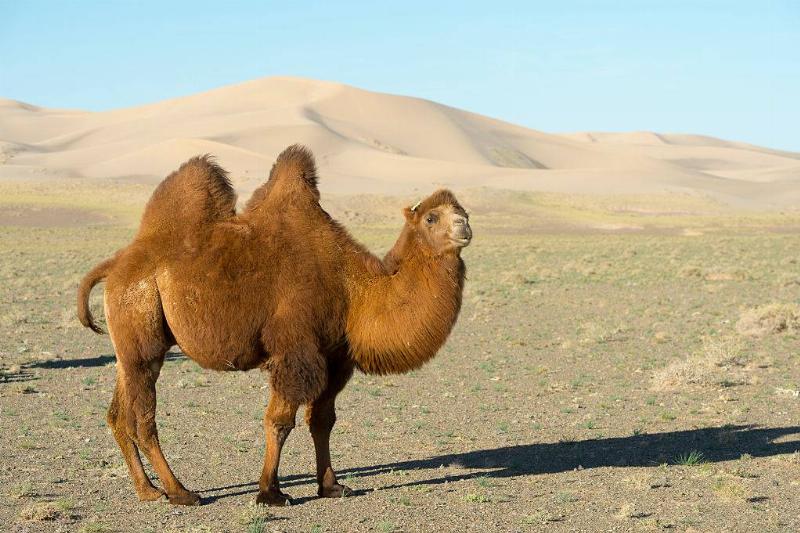

Source: Wolfgang Kaehler/LightRocket via Getty Images
Additionally, camels have highly efficient intestines and kidneys which allow them to survive in environments where water is scarce. These incredible species are able to tolerate dehydration through the presence of oval-shaped red blood cells that enable them to retain moisture more effectively than other mammals.
Alcohol Consumption Wouldn’t Keep You Warm
Alcohol can give you the perception of warming from cold temperatures, but in reality, it has the opposite effect. Drinking alcoholic beverages can result in a decrease in body temperature due to blood vessels constricting near the skin’s surface.

Source: Robert Alexander/Getty Images
It is important to remember that while alcohol may make you feel warmer in the short term, it will ultimately reduce your ability to maintain a healthy body temperature during cold weather. Therefore, hot chocolate may be a better option when trying to ward off the cold this winter.
The Sun’s Proximity To The Earth Is not Why There Are Seasons
Earth’s distance from the Sun is not solely responsible for the four seasons. Researchers suggest that the tilt of the Earth’s axis, which was likely caused by a collision between Earth and another celestial object, better explains the distinct variations in temperature and environment across the year.

Source: Bettmann/Getty Images
While it is reasonable to assume that proximity to the Sun would influence temperature changes, closer inspection reveals a much more complex relationship between the tilt of the Earth’s axis and seasonal change.
Early Greek Statues Weren't Often Colorless
Polychromy, a practice in which sculptures are decorated with vibrant colors, was a common practice in ancient Greece, but this tradition has been long forgotten. You may be wondering why most recovered statues appear lacking in color.
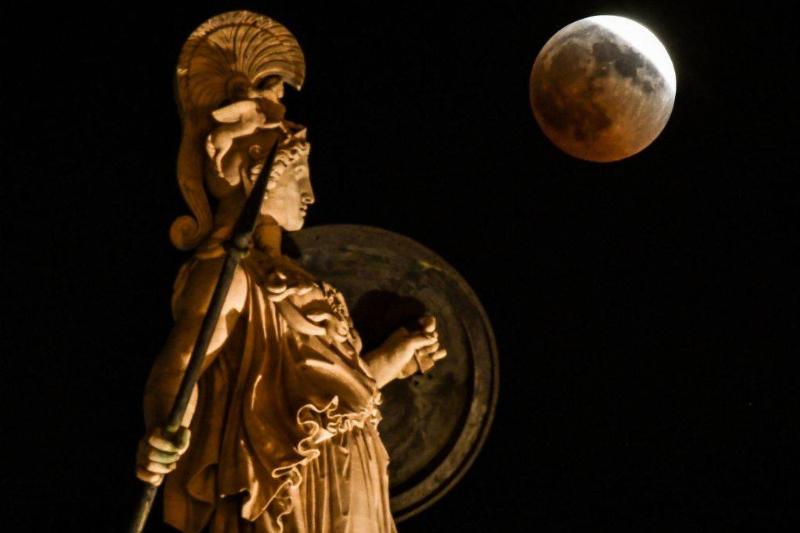

Source: ARIS MESSINIS/AFP via Getty Images
Consequently, if we could take a time machine and travel back to the original sites of these statues, we’d find evidence of their original vibrancy still present. However, by the time of their discovery, their colors had been lost due to aging, exposure, and dirt.
Snakes Can't Always Unhinge Their Jaws.
It’s unclear how a snake can absorb other creatures longer than it is. Nevertheless, researchers now believe they are familiar with some of the reptile’s supersizing techniques. Contrary to popular perception, snakes cannot unhinge their jaws.
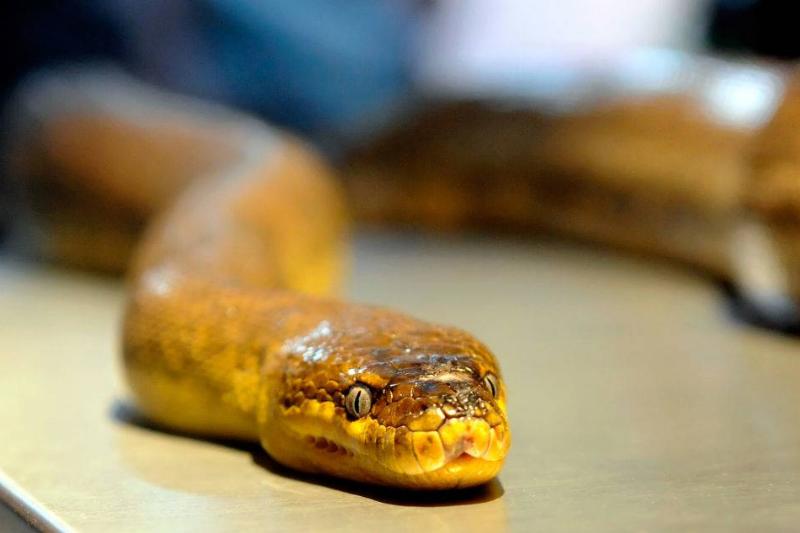

Source: Ethan Miller/Getty Images
Instead, their upper and lower jawbones are separated by elastic ligaments that allow them to open their mouths much wider than other animals. This is remarkable—however, snakes lack the capability to actually unhinge their jaws to swallow large prey.
Red Does Not Put Bulls In A Frenzy
It’s a widespread misconception that bulls hate the color red. In fact, bulls can’t actually see the color red, or any color, because they are colorblind. When you watch a bull charging at a matador, it is the matador’s actions that are provoking the animal, not their clothing.
Source: Drew Angerer/Getty Images
Although the characteristic red cape has become something that a crowd might expect to see as part of this scene, it is a detail without any real influence on the bull’s behavior.
Our Blood Does Not Become Blue Without Oxygen
The idea that veins are blue because they carry blood without oxygen has become widespread. Though the blood circulating inside our veins may appear blue at first glance, it is always red. The intensity of the redness of the blood is determined by its oxygenation levels, ranging from light to dark.
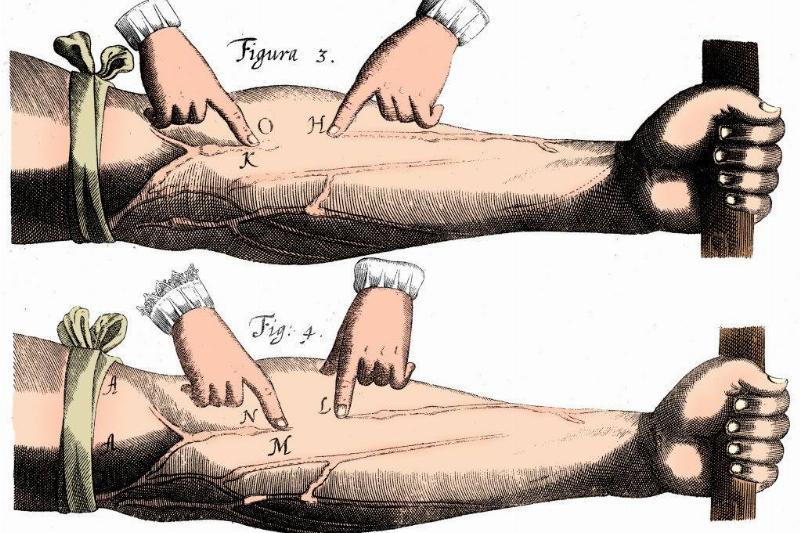
Source: The Print Collector/Getty Images
What truly makes our veins appear blue is a phenomenon known as structural coloration. When exposed to light, our skin reflects the light back as a particular wavelength, resulting in our eyes picking up a blue hue.
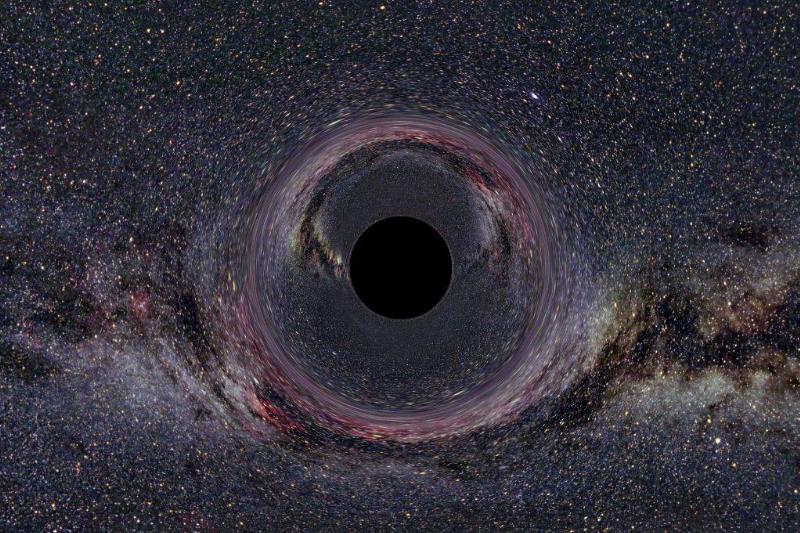
Black Holes Don’t Have An Infinite Gravity Pull
Even though we have never directly seen a black hole, we still know that they exist and that they have some strange effects on space and time. Because black holes are strange, they are sometimes thought to have a perpetual gravitational force.

Source: Photo 12/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
While it is true that their immense pull can quickly draw nearby objects in, the danger of those objects being pulled into a black hole from a safe distance is negligible. Observing black holes from afar can still be a mesmerizing experience, however.
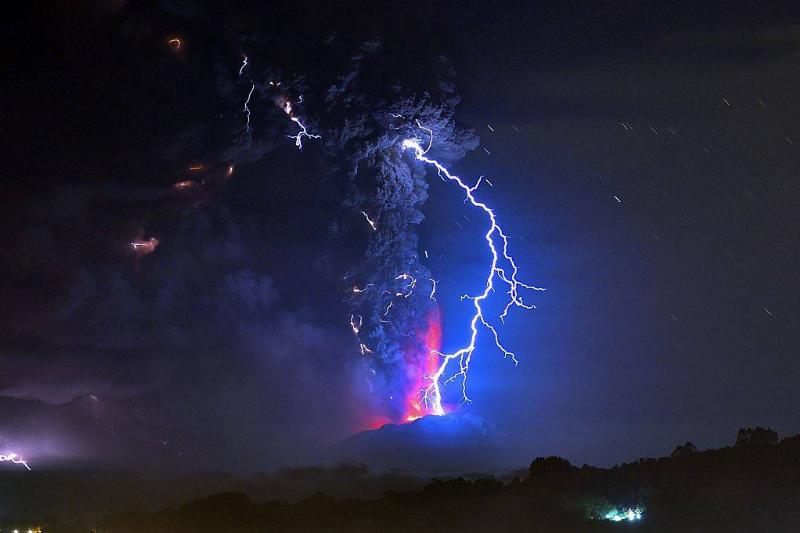
Lightning Can Hit The Same Spot Twice
Lighting does not discriminate when it comes to its targets—particularly if there is a towering, lone object in range. It can strike the same place any number of times. Consider the Empire State Building in New York, which experiences strikes, on average, 23 times every year.

Source: MARTIN BERNETTI/AFP via Getty Images
Even if the sky is blue, if you can hear thunder, lightning could be close enough to present an imminent threat. When thunder rumbles, run for cover. Where did the proverb “lightning doesn’t strike twice” come from? A headline from the Melbourne Daily Newspaper from 1851 is probably to blame.
There Are No "Taste Sectors" in Your Tongue.
Do you recall trying to place various foods on various sections of your tongue to see which part tastes what? The tongue map idea is frequently taught in schools. The idea that the distinct flavor sectors of salty, sour, sweet, and bitter are located on different parts of the tongue was developed by a German scientist in 1901.
Source: Koichi Kamoshida/Getty Images
This theory, however, has since been debunked. In actuality, all taste buds can distinguish between these four flavors (or five if you count umami! ), which include salty and sour.
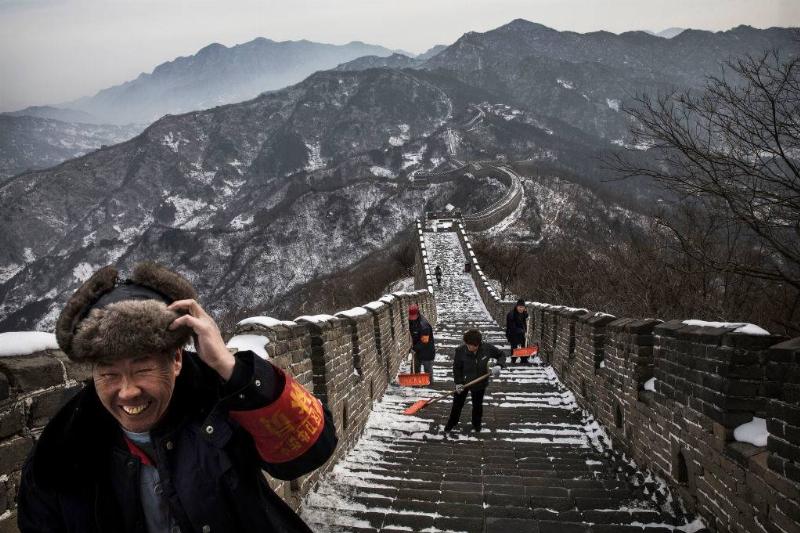
The Great Wall of China Can't Be Seen from Space
This one has evolved into a cosmic-sized myth. Due to its extraordinary span, the Great Wall of China is said to be visible from space. Astronauts who have been to space report that they can see cities from their orbital view. However, it’s unlikely that they would be able to discern the length and breadth of the Great Wall.

Source: Kevin Frayer/Getty Images
This was confirmed by Yang Liwei, a Chinese astronaut who attempted to identify the Great Wall with the naked eye but was unsuccessful. Nonetheless, many man-made structures can still be seen clearly from Earth’s surface.
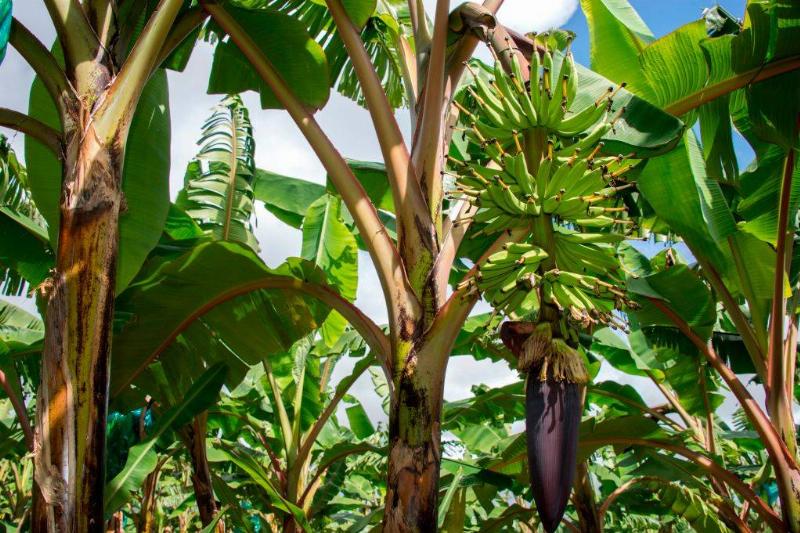
Bananas Aren't a Type of Tree
Bananas may look like fruits, but they are actually berries. The plant they come from usually reaches heights of 25 feet, which makes it the world’s largest perennial herb. It’s no wonder people are often surprised to learn that sweet bananas grow on a giant herb and not on trees.

Source: HELENE VALENZUELA/AFP via Getty Images
Most varieties of bananas don’t produce mature seeds, so even though their exterior looks like a fruit, technically, they are classified as berries. Don’t worry, though—they won’t be out of place in a fruit bowl.
